How to test vanadium redox flow battery cells on Neware battery cyclers?
Vanadium Redox Flow Batteries (VRFBs) are advanced, long-duration energy storage systems that use vanadium ions in different oxidation states within an electrolyte to store and release electrical energy via a reversible electrochemical reaction. They are ideal for large-scale, stationary grid storage due to their long,, non-degrading lifespan (>20 years), safety (non-flammable), and ability to independently scale power (cell stack size) and energy (tank volume).
- Electrolyte: A mixture of vanadium sulfate and sulfuric acid (or similar) is used in both the catholyte and anolyte tanks.
- Membrane: An ion-exchange membrane (e.g., Nafion) separates the two electrolyte halves, allowing ions to pass while preventing cross-contamination of the vanadium species.
- Electrodes: Porous carbon felt or graphitic materials are used to provide high surface area for the electrochemical reaction, often with specialized bipolar plates to manage flow.
- Cell Stack: The core structure where multiple cells are stacked in series to increase voltage and power.
- Mechanism: Pumps circulate the liquid electrolyte from storage tanks through the cell stack, where vanadium changes oxidation states (V2+/V3+cap V raised to the 2 plus power / cap V raised to the 3 plus power 𝑉2+/𝑉3+ on the negative side, V4+/V5+cap V raised to the 4 plus power / cap V raised to the 5 plus power 𝑉4+/𝑉5+ on the positive side).
- Capacity: Because the energy is stored in the liquid, capacity can be increased simply by increasing the size of the storage tanks.
- Durability: Unlike lithium-ion, VRFBs can be fully discharged without damage and experience negligible capacity loss over thousands of cycles.
- Efficiency: Lab-scale cells can achieve high performance, with reports of coulombic efficiency around 97% and overall energy efficiency frequently above 70%.
- Energy Density: Lower than lithium-ion batteries, making them heavy and bulky.
- Upfront Cost: While long-lasting, the high cost of vanadium can make them more expensive initially, although they are cheaper in terms of long-term, large-scale storage.
- Complexity: Require pumps and plumbing for electrolyte circulation.

How to test vanadium redox flow battery cells on Neware battery cyclers?
First, Neware BTS4000 Set up
Login
Click the software icon BTS8.0.0 or BTS8.0.1 (see Figure 1). Navigate to the “User” menu at the top of the interface and click “User Login.” In the “Login” window, enter the “Username” and “Password” (the software provides an initial username: admin and initial password: neware.
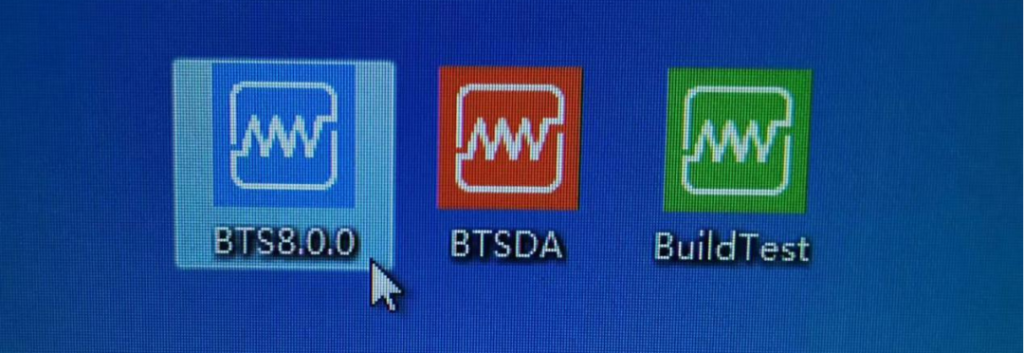
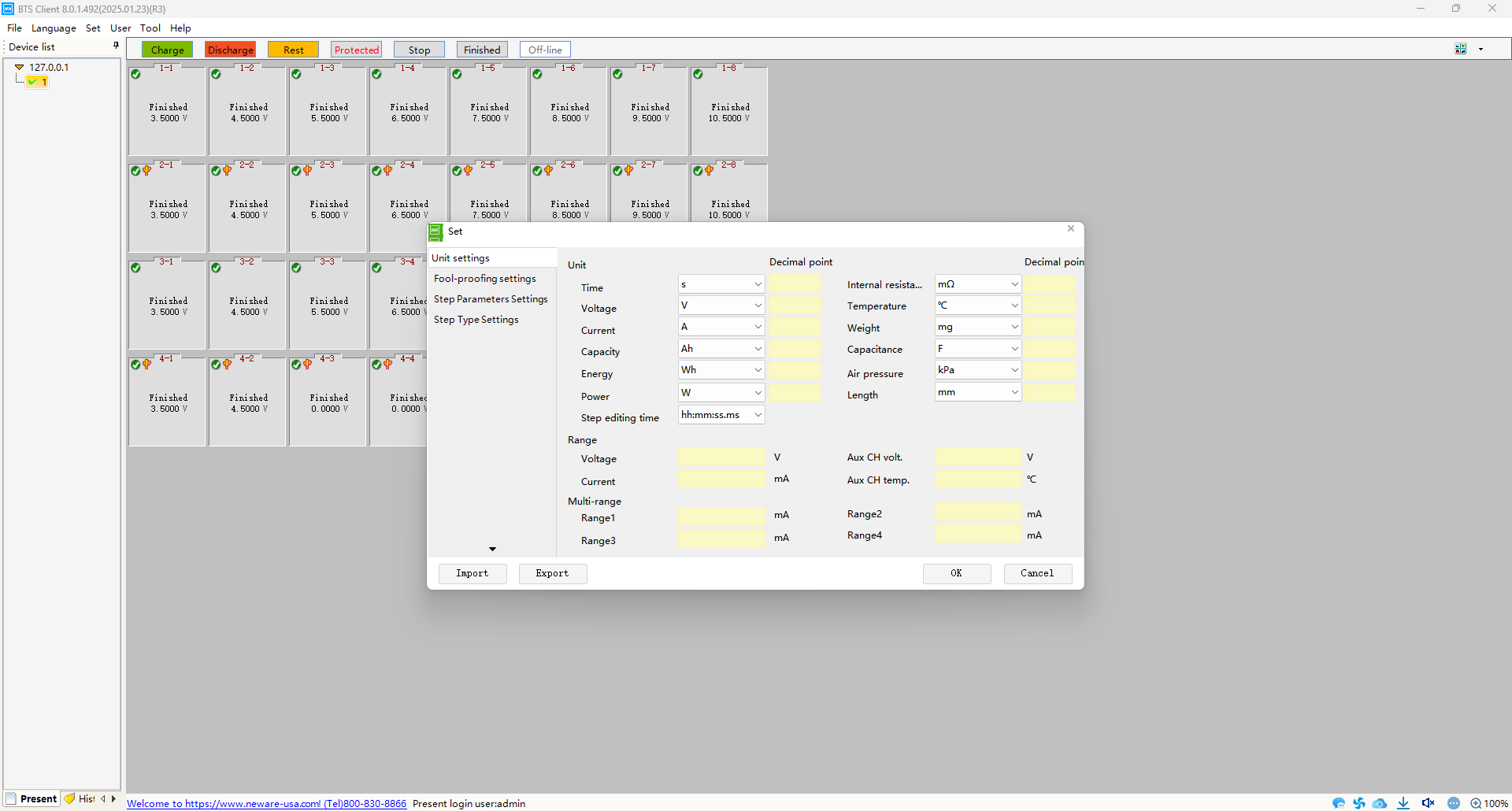
Unit Customization: For unit settings, if accuracy is not critical, refer to Figure 3. In range settings, focus primarily on voltage, auxiliary channel voltage, and current. Set these values according to the battery parameters being tested, ensuring they exceed the voltage and current limits during charging and discharging. Note: The unit customization interface allows setting units for parameters such as voltage, current, and power. For example, current can be set to μA, mA, A, or kA. Alternatively, the unit customization interface can be accessed by right-clicking on a channel and selecting “Unit settings.”
Figure 4 shows an example of setting up a 6-cycle constant current charge-discharge program for a vanadium redox flow cell (active area: 2cm*2cm) at 240mA (current density 60mA/cm²). In this example, the charge/discharge cutoff condition is set to voltage cutoff, and the resting cutoff condition is set to time cutoff. Note the recording conditions—time interval—on the right side of the figure. Note: Protection values can also be set as needed.
Setting up an integrated flow cell testing system (YTH-1)
Preparation:
(1) Correctly install the proton exchange membrane and electrodes on the single-cell clamp, ensuring no leakage. After assembly, remove the metal positioning rod;
(2) Inject 20 mL of 3.5-valent vanadium battery electrolyte into each of the positive and negative electrode storage tanks. Purge the negative electrode storage tank with nitrogen for protection;
(3) Following the tutorial in Section 1 of this document, install the Xinwei charge/discharge tester software on the computer. Connect the lower-level machine, the middle-level machine, and the computer via network cable to ensure normal communication;
(4) Connect the Xinwei charge/discharge tester’s positive and negative alligator clips (red: positive, black: negative) to the corresponding positive and negative copper plates of the single-cell clamp (before charging, do not distinguish between positive and negative electrodes);
The configuration of the integrated flow cell testing system (YTH-1) is shown in Table 1.
| Item | Specification | Remarks |
| Single Cell Fixture | Model: LSB-1 | Active Area: 2cm * 2cm |
| Electrolyte Concentration | 1.7M V3.5+ + 4.7M H2SO4 | 3.5-valence vanadium battery electrolyte used for both positive and negative electrodes |
| Electrolyte Volume | 20mL of 3.5-valence electrolyte for each electrode | Negative electrolyte storage tank protected by nitrogen filling |
| Peristaltic Pump | Positive and negative peristaltic pumps at 150Hz | |
| Membrane | 50-micron perfluorosulfonic acid proton exchange membrane | |
| Electrode | 4.35mm high-activity graphite felt | |
| Charge-Discharge Tester | Neware | 5V6A, with negative power supply. It can discharge batteries to 0V. |
| Temperature Controller | / | / |
Step 1: Rest, time: 30 seconds;
Step 2: Constant current charging, current: 5000mA, charging cut-off voltage: 1.6V;
Step 3: Constant current discharging, current: 5000mA, discharging cut-off voltage: 1.0V;
Step 4: Cycle, starting step: Step 1, number of cycles: 100;
For reference only!!!
How a Vanadium Redox Flow Battery Works
Due to the limited knowledge and English level is inevitable errors and omissions, if there are errors or infringement of the text, please contact me as soon as possible by private letter, I will immediately be corrected or deleted.
Neware was founded in 1998. We are trusted by ATL, BYD, CATL, Tesla, Apple, HUAWEI, SolarEdge, etc. We provide battery testing solutions for testing battery cell, module, pack, supercapacitor, BESS, etc. If you want to do capacity, cycle life, pulse, DCIR, GITT, HPPC, or EV driving simulation test, please feel free to contact us.