Routine Electrochemical Testing of Solid-State Electrolytes
Routine Electrochemical Testing of Solid-State Electrolytes
Google Gemini’s answer is
In solid-state battery research, a series of standardized electrochemical tests are conducted to fully evaluate the performance of solid-state electrolytes (SSEs). These tests characterize ion transport, electrochemical windows, interfacial stability, and dendrite suppression capabilities.
- Ionic Conductivity Testing Measured via Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) using symmetric stainless steel cells. The bulk resistance is determined from the high-frequency intercept on the Nyquist plot and used to calculate conductivity based on sample dimensions.
- Electronic Conductivity Testing Conducted using DC polarization (blocking electrode method). By applying a small constant voltage and measuring the leakage current, the electronic conductivity is evaluated. For high-performance SSEs, this value must be several orders of magnitude lower than the ionic conductivity.
- Electrochemical Window Testing Typically performed using Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV). By increasing the voltage until a significant oxidation current is observed, the electrochemical stability window is defined, which determines compatibility with high-voltage cathodes.
- Li-ion Transference Number Testing Commonly evaluated using the Bruce-Vincent method. It involves recording the impedance and steady-state current of a Li symmetric cell before and after DC polarization to calculate the fraction of current carried by lithium ions.
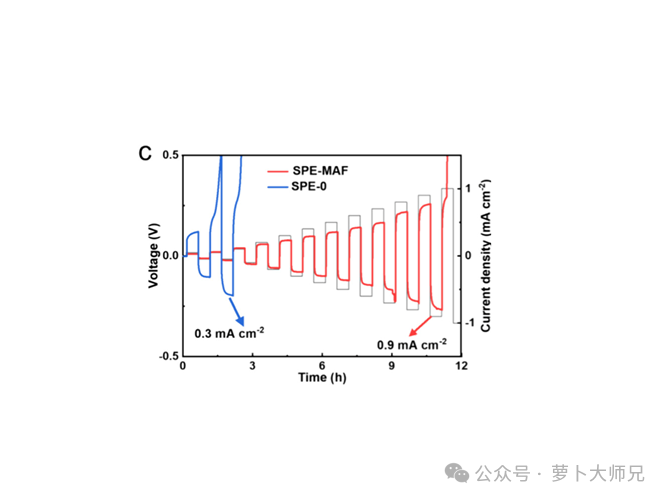
- Critical Current Density (CCD) Testing Performed by cycling a Li symmetric cell with incrementally increasing current densities. The CCD is the threshold where a sudden voltage drop or oscillation occurs, indicating dendrite penetration.
- Interfacial Impedance Evolution Monitoring changes in impedance at the electrolyte/electrode interfaces over time or cycling via in-situ EIS to assess the chemical and mechanical stability of the interface layers.
The following sharing comes from a researcher working on battery research. For reference only!!!
The source is the WeChat public account “Brother Radish”. 微信公众号 萝卜大师兄
Ionic Conductivity (SS//SS Symmetric Cell) The ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolyte membrane is calculated using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) and the membrane thickness.
Lithium-ion Transference Number (Li//Li Symmetric Cell) The lithium-ion transference number of the polymer electrolyte membrane is calculated via chronoamperometry combined with the interfacial resistance measured before and after polarization.
Electrochemical Stability Window (Li//SS Asymmetric Cell) The stable voltage window of the polymer electrolyte membrane is determined through Linear Sweep Voltammetry (LSV) to analyze its high-voltage oxidation resistance.
Activation Energy (SS//SS Symmetric Cell) By measuring EIS at various temperatures, the corresponding ionic conductivities are calculated. The activation energy is then derived by plotting the logarithm of conductivity against temperature (Arrhenius plot) according to the Arrhenius equation.
Plating/Stripping Cycling Test (Li//Li Symmetric Cell) Galvanostatic charge-discharge tests are performed using battery testing channels. Tests are typically conducted at low current densities, high current densities, and current densities equivalent to the actual battery cycling rates.
Critical Current Density (CCD) (Li//Li Symmetric Cell) Similar to the plating/stripping cycling test, this procedure is used to determine the critical current density (CCD) of the polymer electrolyte membrane. ———->Critical Current Density (CCD) Test Procedure Setup
(In-situ) EIS at Different Cycling Stages (Li//Li Symmetric Cell) EIS measurements taken after specific numbers of plating/stripping cycles can analyze the protective effect of the electrolyte membrane on the lithium anode. This is ideally combined with XPS analysis of the lithium metal surface after cycling, or TOF-SIMS if conditions permit.
Li-Cu Coulombic Efficiency Test (Cu//Li Asymmetric Cell) The Coulombic efficiency is measured through galvanostatic charge-discharge tests using battery testing channels to evaluate the reversibility of lithium deposition on a copper substrate.
Li//Cathode Half-Cells:
- High/Low Rate Cycling and Rate Capability Tests: This allows for a more detailed analysis of Galvanostatic Charge-Discharge (GCD) profiles. By comparing profiles at different cycle numbers or rates, one can analyze changes in polarization voltage, the depression of discharge plateaus, and other performance metrics.
- Cyclic Voltammetry (CV): This can be used to analyze current stability. CV curves at scan rates between 0.1 and 0.5 mV/s are typically used to calculate the lithium-ion diffusion coefficient and to analyze the polarization voltage of the system.
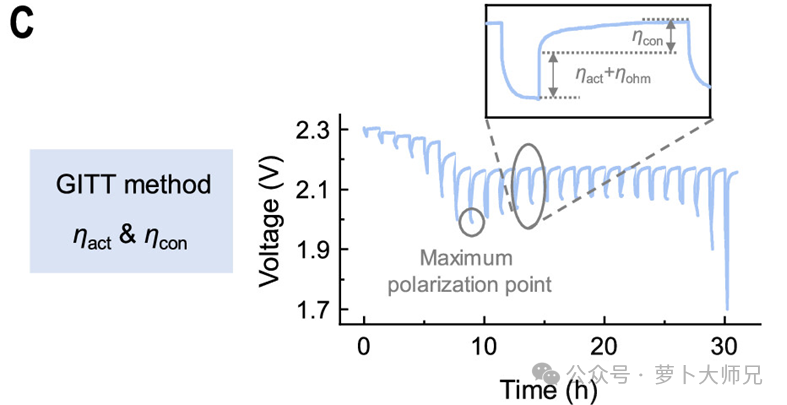
- Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique (GITT): This is employed to calculate the lithium-ion diffusion coefficient. Depending on the specific cathode system, other thermodynamic and kinetic analyses can also be performed. Use Neware battery cyclers test GITT.
More: How to set GITT test on Neware BTS for lithium-sulfur batteries?
- Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): EIS can be measured before and after cycling to analyze the protective effect on the lithium anode. In-situ EIS can also be performed, as discussed in the previous section (please refer to the earlier descriptions for details).
Reference: Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201205.
Due to the limited knowledge and English level is inevitable errors and omissions, if there are errors or infringement of the text, please contact me as soon as possible by private letter, I will immediately be corrected or deleted.