What is Battery Electrolyte?
A battery electrolyte is an integral constituent of your battery responsible for carrying ions (both positively and negatively charged between the cathode and anode.
It is often available in liquid or paste-like form and it ensures that your battery has a neutral charge at all times.
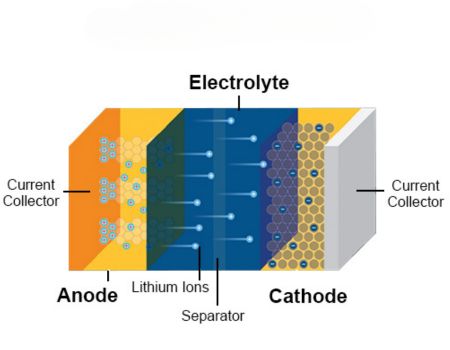
Importance of Electrolytes in Batteries
The electrolyte is undoubtedly one of the most significant constituents of your battery. It is renowned for its primary function, which revolves around ion conduction. However, this versatile substance serves other essential functions.
· Ion Conduction
Primarily, a battery electrolyte is tasked with ferrying charged atoms between your battery’s two primary terminals (the cathode and anode).
By accomplishing this role, the electrolyte ensures that there is conduction of electric current. This consequently allows your battery to discharge and recharge.
· Chemical Reactions
The primary operations of your battery, that is, charging and discharging, are centered on chemical reactions. These chemical reactions are facilitated by the electrolyte, which is often chemically stable. This mitigates unprecedented reactions, which may severely damage other essential components of your battery.
· Separation
The cathode and the anode are two of the most pivotal constituents of your battery and they harbor the charged ions responsible for your battery’s operation. Contact between these two terminals can have severe consequences, which include short-circuiting. The electrolyte lies between these two stations, ultimately serving as a separator and a bridge.
Types of Battery Electrolytes
Batteries have found their way into most of the gadgets you interact with daily and they come in distinct forms. These distinct battery options are endowed with varied constituents, such as the electrolyte. Today’s batteries utilize the following types of electrolytes;
Liquid Electrolytes
Liquid electrolytes are characterized by their free-flowing nature, which makes them perfect for ferrying ions between the anode and cathode. They are further divided into;
Aqueous Electrolytes
This type of electrolyte has been broadly exploited for years owing to its effectiveness and relative affordability.
It is distinguished by its reliance on water as the primary solvent. Aqueous electrolytes are quite prominent in nickel-cadmium and lead-acid batteries. However, their use in other battery types is limited by their low electrochemical stability.
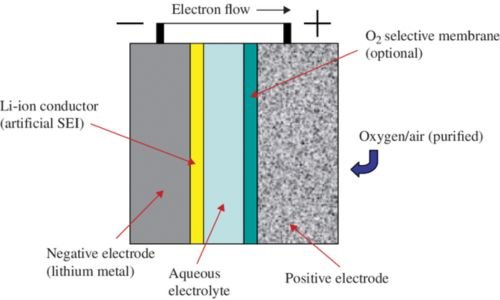
Non-aqueous Electrolytes
Non-aqueous electrolytes are renowned and revered for their comparatively superior energy densities hence they are often deployed in lithium-ion batteries. They utilize organic solvents and are compatible with numerous electrode materials. However, you should be cautious when using non-aqueous solvents since they are quite flammable.
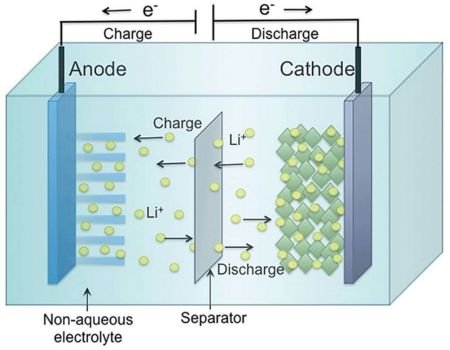
Advantages of Liquid Electrolytes
- Superior Ion Conductivity: If your battery features a liquid electrolyte, you will enjoy faster ionic conduction due to the free-flowing nature of these electrolytes. This will make your battery faster at powering your devices and recharging.
- Cost-Effective: Liquid electrolytes are quite simple and their production does not necessitate expensive materials. This translates into relatively lower prices.
- Reduced Internal Resistance: Batteries utilizing liquid electrolytes are less susceptible to unprecedented energy losses making them quite efficient.
- Excellent Thermal Management: Liquid battery electrolytes are capable of dispensing excess heat thus permitting their deployment in high-power batteries.
Limitations
- Reduced Energy Density: Owing to the relatively lower volume and weight of liquid electrolytes, their energy output is comparatively lower.
- Risk of Leakage: Once a battery reliant on liquid electrolytes gets physically damaged, electrolyte spillage may occur. This can be a safety concern.
Solid Electrolytes
Solid electrolytes are gradually taking over the electrolyte market thanks to their safety profile and relatively superior energy density. They are available in distinct forms including;
- Ceramic Electrolytes: They feature ceramic as the principal construction material making them extremely safe. They also boast impressive ion conduction rates but are quite expensive.
- Polymer Electrolytes: Polymer electrolytes feature ionic salts, which equip them with moderately high ionic conductivity rates. Their prominence can be attributed to their non-flammable nature.
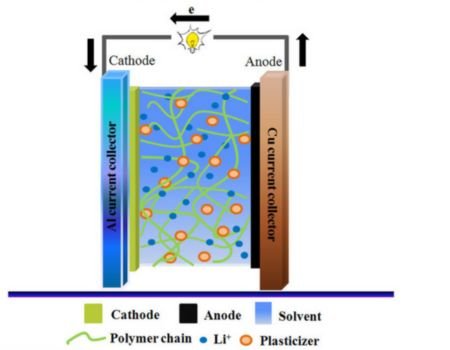
Advantages of Solid Electrolytes
- Better Thermal Stability: Batteries reliant on solid electrolytes are more suitable for high-power applications since they can tolerate extreme temperatures.
- Enhanced Safety: Most solid electrolytes are manufactured from non-flammable materials like polymers and ceramics. This makes your battery less susceptible to fires.
- Higher Energy Density: The high volume and weight of solid electrolytes translates into a higher power storage capacity. This means you can utilize your battery for longer or power-demanding appliances.
- Longer Lifespan: Solid electrolytes are not susceptible to leakages and are quite tolerant to abrasion. This translates into longer charge and discharge cycles for you.
Limitations
- Relatively Lower Ion Conduction: Compared to their liquid counterparts, they move ions slightly slowly. This results in relatively slower charge and discharge rates.
- Compatibility Issues: The majority of solid electrolytes available today work with limited electrode materials. This limits their possible applications.
Gel Electrolytes
Gel electrolytes are half solid-half liquid electrolytes made by blending liquid electrolytes with a solid matrix. This unique combination elevates their mechanical stability while shrinking the possibility of spillage or leakage. Gel electrolytes are often employed in electric vehicle batteries due to their high vibration tolerance.
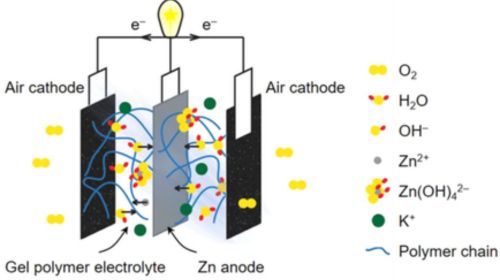
Advantages of Gel Electrolytes
- Impressive Energy Density: Their structure allows them to pack more energy than most liquid electrolytes.
- Improved Stability: The incorporation of a solid or semi-solid matrix in their makeup elevates their mechanical stability. This means that your battery can stomach moderate impacts or vibrations.
- High Ionic Conductivity: Gel electrolytes are partly liquid meaning they are quite good at transmitting ions. This makes them fast at charging and discharging.
- Improved Safety: Their semi-solid state eliminates the risk of electrolyte spillage while also elevating their resistance to fires and explosions.
Limitations
- Limited Temperature Range: If you deploy your gel-electrolyte battery in an extremely cold or hot environment, its performance may deteriorate. This is because extreme temperatures alter the gel electrolyte’s makeup.
- Complex Manufacturing Process: Manufacturing gel electrolytes is relatively more sophisticated than manufacturing liquid or solid electrolytes. This results in comparatively higher price tags.
Best Electrolytes for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries have found their way into most residential, commercial, and industrial applications necessitating a power storage solution. This is down to their impressive energy density, which is partly a consequence of the electrolytes they exploit. The most prominent lithium-ion battery electrolytes include.
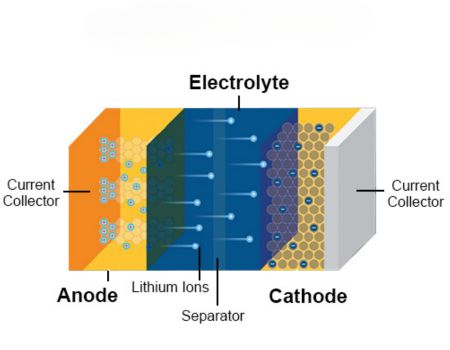
- Lithium Hexafluorophosphate: These electrolytes consist of organic solvents like dimethyl carbonate, which gives them superior ion conductivity. LiPF6 electrolytes are revered for their high stability and compatibility with the most frequently used electrode materials in lithium batteries. Its use is however limited by its vulnerability to moisture reaction.
- Lithium Tetrafluoroborate: This electrolyte is prominently deployed in high-performance lithium-ion batteries due to its impeccable stability even at temperatures as high as 120°C. It is perfect for high-voltage cathodes but its use is limited by its relatively higher price tag.
- Lithium Perchlorate: Batteries reliant on lithium perchlorate as the electrolyte guarantee you better performance levels due to its good conductivity. It has a broad electrochemical window but is highly hygroscopic, which makes it a concern for the environment.
Best Electrolytes for Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries have provided power preservation solutions to many for well over 100 years. Their prominence has been driven by their simplicity and effectiveness, which is partly facilitated by the electrolyte they exploit. Lead-acid batteries are synonymous with the following electrolytes.
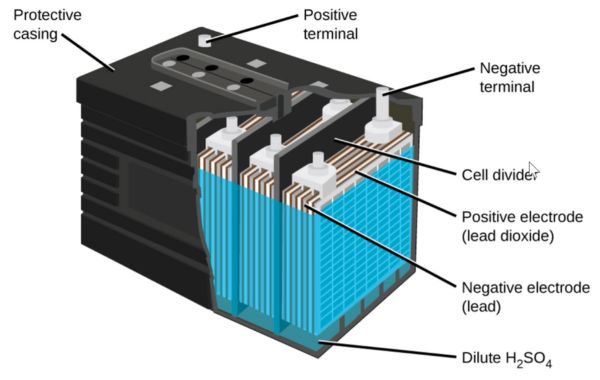
- Sulfuric Acid: Sulfuric acid provides a suitable platform for essential chemical reactions to occur in your battery. It also boasts an impressive ionic conductivity rate and can be procured cheaply. This has made it the primary electrolyte in lead-acid batteries and it is often comprised of 35-40% H2SO4 and distilled water.
- Gel Electrolyte: Gel electrolytes are slowly growing popular, especially in lead-acid batteries. They are primarily made of H2SO4 acid and silica, which is a strong gelling agent. This electrolyte makes your battery mechanically stable and eliminates the risk of electrolyte leakage.
Best Electrolytes for Nickel Metal Batteries
Part of the reason why nickel metal batteries are quite popular today is their unique electrolyte composition. They primarily rely on aqueous potassium hydroxide but in recent years other electrolytes have been experimented with. Your nickel metal battery may exploit the following electrolytes;
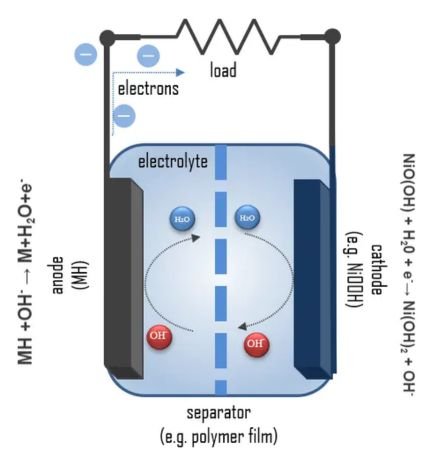
- Potassium Hydroxide (KOH):This is the historical electrolyte deployed in nickel metal batteries. It is simply made of distilled water and potassium hydroxide at a concentration of 25-35%. This electrolyte works well with both the positive and negative electrodes leading to impressive ion conductivity.
- Phosphoric Acid: Phosphoric acid is primarily used in nickel metal batteries with an iron oxide cathode and a nickel oxide anode. Although this electrolyte type is not as popular as the potassium hydroxide electrolyte, it is quite effective and stable.
Best Electrolytes for Alkaline Batteries
Alkaline batteries are durable batteries fitted into your household electronics including remotes. These indispensable components are revered for their high energy density and lengthier charge cycles. They primarily rely on potassium hydroxide (KOH) as the dominant electrolyte, which makes them makes them chemically stable.
Best Electrolyte for Zinc-Air Batteries
Zinc-air batteries have become household names in distinct electronic gadgets, especially portable electronics like hearing aids. They are available in distinct forms and each form utilizes a varied type of electrolyte. Your zinc-air battery may exploit one of the following electrolytes;
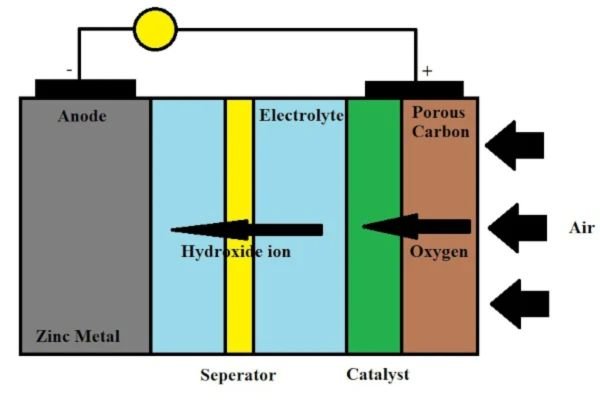
- Potassium hydroxide
- Lithium hydroxide
- Sodium hydroxide
What Makes Up Battery Electrolytes
Although varying batteries exploit distinct electrolytes, the majority of these electrolytes exhibit a similar configuration and makeup. This unique makeup allows them to fulfill their primary role, ion conduction, diligently and sufficiently. Here is a breakdown of your battery’s electrolyte.
· Solvent
Each battery electrolyte consists of a solvent, which essentially acts as the conduit for ion conduction. High-quality batteries utilize solvents synonymous with high dielectric constants and this makes them faster at charging and discharging. Some of the prominently exploited solvents include;
- Propylene carbonate.
- Ethylene carbonate.
- Dimethyl carbonate.
· Salt
Battery electrolytes may be injected with varying salts and the type of salt dispensed determines the conductivity of your battery. Once the salt is dispensed into your electrolyte’s solvent, it segregates consequently producing ions, which ferry the electric charges. Commonly utilized salts include lead-sulfate and lithium salts.
· Additives
Quite often, electrolytes in batteries are injected with specific doses of additives to supplement or complement certain features. These additives elevate certain features in your battery including thermal stability and electrode passivation. Some prominently exploited additives include;
- Flame retardants.
- Electrolyte stabilizers.
- Conductive salts.
- Viscosity modifiers.
Conductive Fillers
In batteries utilizing electrolytes with a relatively lower conductivity rate, conductive fillers are often injected. These fillers simply elevate the electrolyte’s ability to ferry ions and strengthen the compatibility of the electrolyte with the electrodes. Commonly exploited conductive fillers include graphene and carbon black.
The constituents utilized to manufacture the electrolyte and their respective concentration greatly impact your battery’s performance. This explains why it is important to strike a balance between the materials and their respective concentrations. They can impact the following properties of your battery:
- Voltage: Although higher solvent and salt concentrations result in higher voltages, you must be cautious to avoid messing with the battery’s thermal stability.
- Ion Conductivity: If your electrolyte is highly concentrated, it will conduct more ions quickly. However, if it is excessively concentrated, its conduction rate will depreciate due to increased viscosity.Similarly, a lower concentration shrinks your electrolyte’s ion conductivity.
- Safety: The inclusion of certain materials, be it solvents, salts, or additives may increase or decrease your battery’s safety profile. For instance, injecting a flame retardant into a liquid electrolyte eliminates the risk of fires and explosions.
Factors Impacting the Performance of Battery Electrolytes
Electrolytes are indispensable constituents of batteries thus their composition and concentration hugely impact battery performance. Similarly, numerous factors impact how effective the electrolyte is.
- Temperature: Distinct battery electrolytes demonstrate varying temperature tolerance ranges. Subjecting your battery to temperatures beyond this range is likely to lower your battery’s performance. For instance, high temperatures may alter your electrolyte’s viscosity resulting in lower ionic conductivity.
- Composition: The components that make up your electrolyte as well as their respective concentration hugely influence the conductivity of your battery. The type of solvent deployed or the choice of salt determines essential parameters like stability and viscosity.
- Additives: Quite often, the makeup of battery electrolytes is supplemented by the inclusion of essential additives. These additives elevate certain features including thermal and chemical stability thereby improving your battery’s performance. However, if the type of additive is inappropriate, this may weaken certain features.
- Electrochemical Stability: If an electrolyte is chemically unstable, it is likely to react with other components of your battery or foreign elements like moisture. This unprecedented reaction can corrode essential parts resulting in poor performance or battery damage.
- Charge Cycles: After years of constant or frequent use, your battery and its essential components begin to degrade. This is because of the numerous charge and discharge cycles you have subjected it to.Numerous cycles bring about the natural aging of your electrolyte.
Choosing the Best Electrolyte for Your Battery
The choice of electrolyte you choose for your battery may hugely impact how effective your battery is. This underlines the essence of weighing the pros and cons of each type before settling on a particular electrolyte.
- Application Specific Requirements: Most importantly, you should begin by outlining what you expect your battery to achieve. Are you looking for a battery with rapid charging features or a battery with high energy density? This will help you pick an electrolyte that allows your battery to fulfill your specific requirements.
- Battery Type: When it comes to batteries, there is not a one-fit-all electrolyte. This means you must first research your battery type and the compatible electrolyte types. For example, if you have a lead-acid battery, you should opt for a sulfuric acid electrolyte.
- Cost: Finding the perfect electrolyte for your respective battery also requires you to deliberate on the cost. The perfect electrolyte should offer you a balance between performance and your financial constraints.
- Safety: Distinct battery electrolytes come with varying safety profiles and this is determined by their composition. Ensure that you opt for an electrolyte that is less prone to fires or other safety hazards.
- Performance Parameters: Look for an electrolyte that boasts impressive parameters like high ionic conductivity and stability. These parameters are mirrored on your battery’s ultimate specifications making it highly reliable.
Common Applications of Battery Electrolytes
Without an electrolyte, your battery would essentially become ornate. Electrolytes are indispensable parts of every battery out there in the world. As such, they are highly revered in numerous applications including;
- Consumer Electronics: They are part of the makeup of battery-powered appliances like vacuum cleaners and cordless power gadgets.
- Portable Electronics: Electrolytes are featured in lithium batteries installed in tablets, laptops, and smartphones.
- Electric Vehicles: Electric vehicles run on power reserved in batteries and these batteries feature either a liquid or solid electrolyte.
- Grid Storage: High-density electrolytes are integral in high-power batteries specialized to preserve grid power.
- Aerospace Applications: A myriad of aerospace applications rely on batteries and these batteries exploit varying electrolytes.
- Car Starter Batteries: The majority of car starter batteries are lead-acid batteries, which primarily rely on sulfuric acid electrolytes.
Source: What is Battery Electrolyte – A Complete Guide
Contact Neware!
