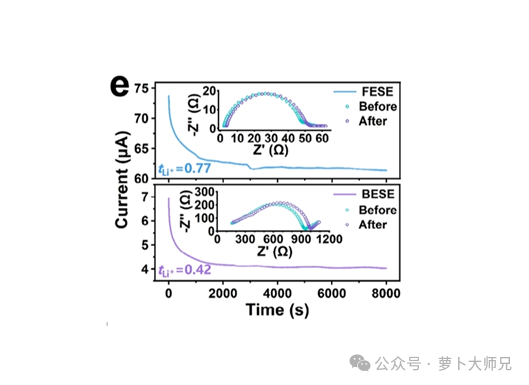
Reference for Li-Cu Battery Testing: Assessing Coulombic Efficiency in Lithium Metal Anodes 2026 post
Reference for Li-Cu Battery Testing: Assessing Coulombic Efficiency in Lithium Metal Anodes Team of Professor Lorenzo Stievano, University of Montpellier, France – Chemistry of Materials Abstract Although lithium metal and anode-free rechargeable batteries (LMBs and AFBs) are phenomenal energy storage systems, the formation of lithium deposits with high surfaces during repeated plating–stripping cycles has hindered their practical applications. Recently, extensive efforts have been made to prevent the growth of high-surface lithium deposition, e.g., electrolyte modification, artificial coating deposition, lithiophilic current collectors, composite lithium metal electrodes, etc. In most of these approaches, Coulombic efficiency (CE) has been used as a quantifiable indicator for the reversibility of the LMBs and AFBs.