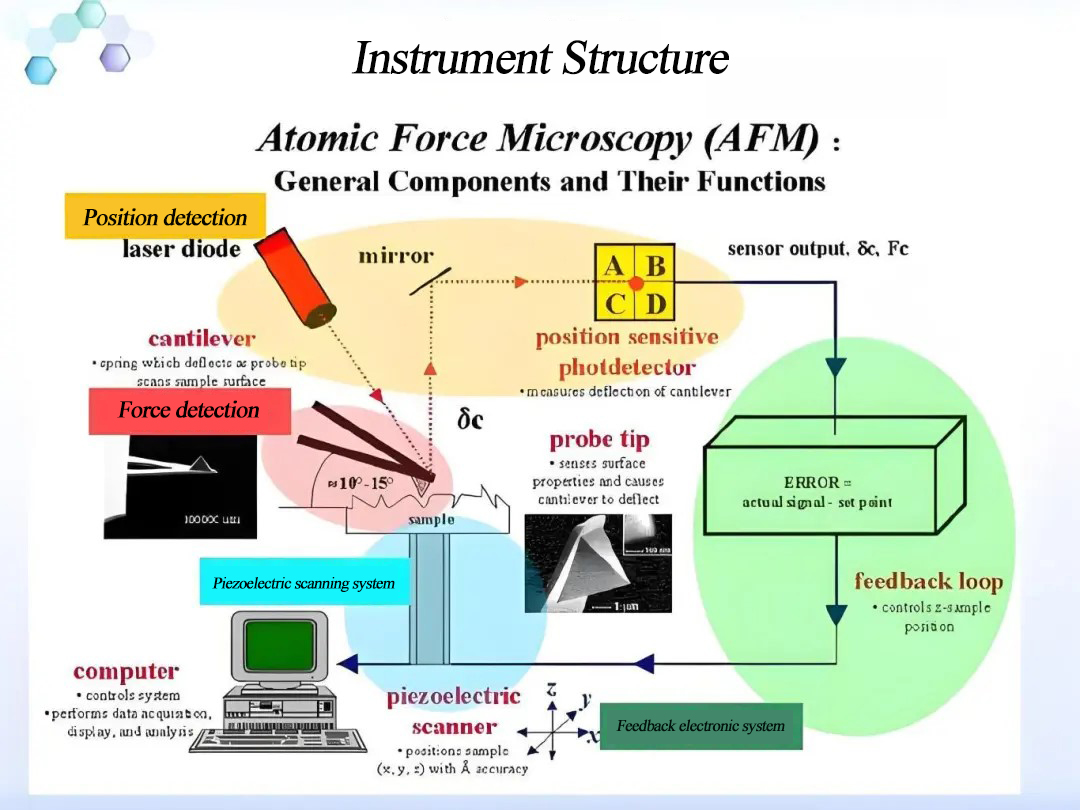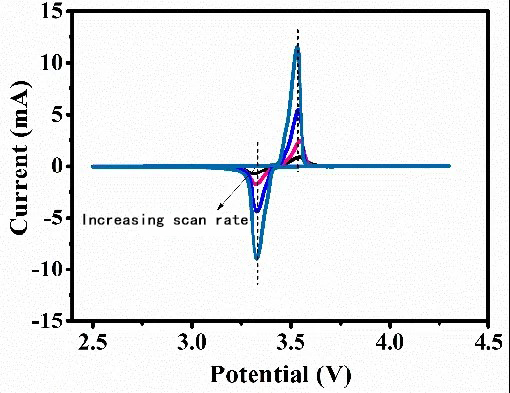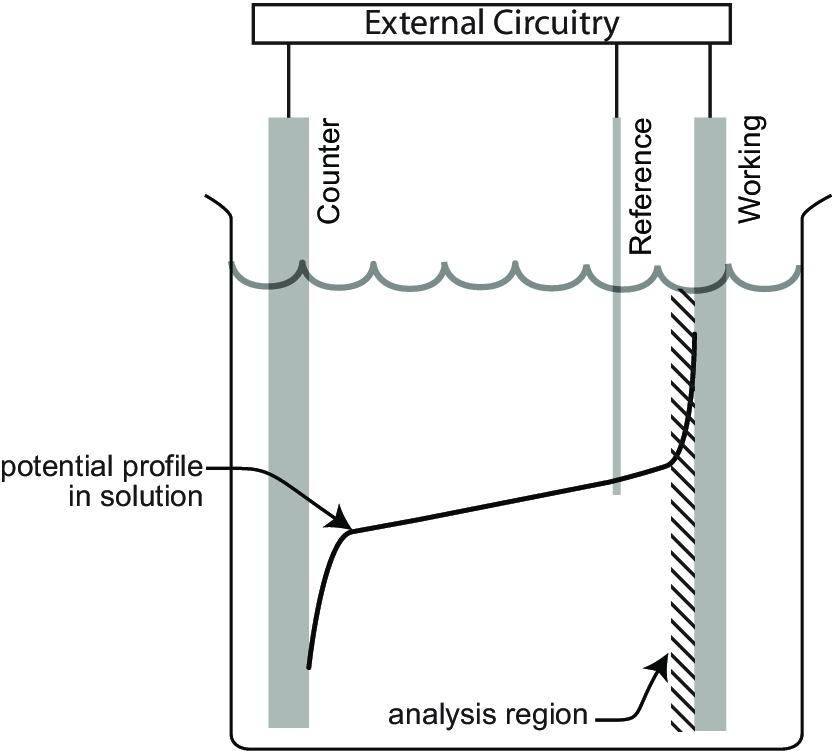
10 mins Guide to the Application and Customization of Three-Electrode Systems In Battery Testing
In the development and production of batteries, the three-electrode test system is an important analytical tool for accurately measuring and analyzing the electrochemical properties of battery electrodes. Compared with the traditional two-electrode system, the three-electrode system can better dissect the electrode behavior and reaction kinetics in batteries, and is therefore widely used in material testing and pole-and-ear cell testing. In this paper, we will introduce in detail the principle, working mechanism, application scenarios, equipment and fixture selection of three-electrode testing, as well as the influence of pole-ear design in three-electrode testing, safety considerations, and the need for equipment features. 1. Three-electrode material testing 1.1 Principle of three-electrode testing A three-electrode