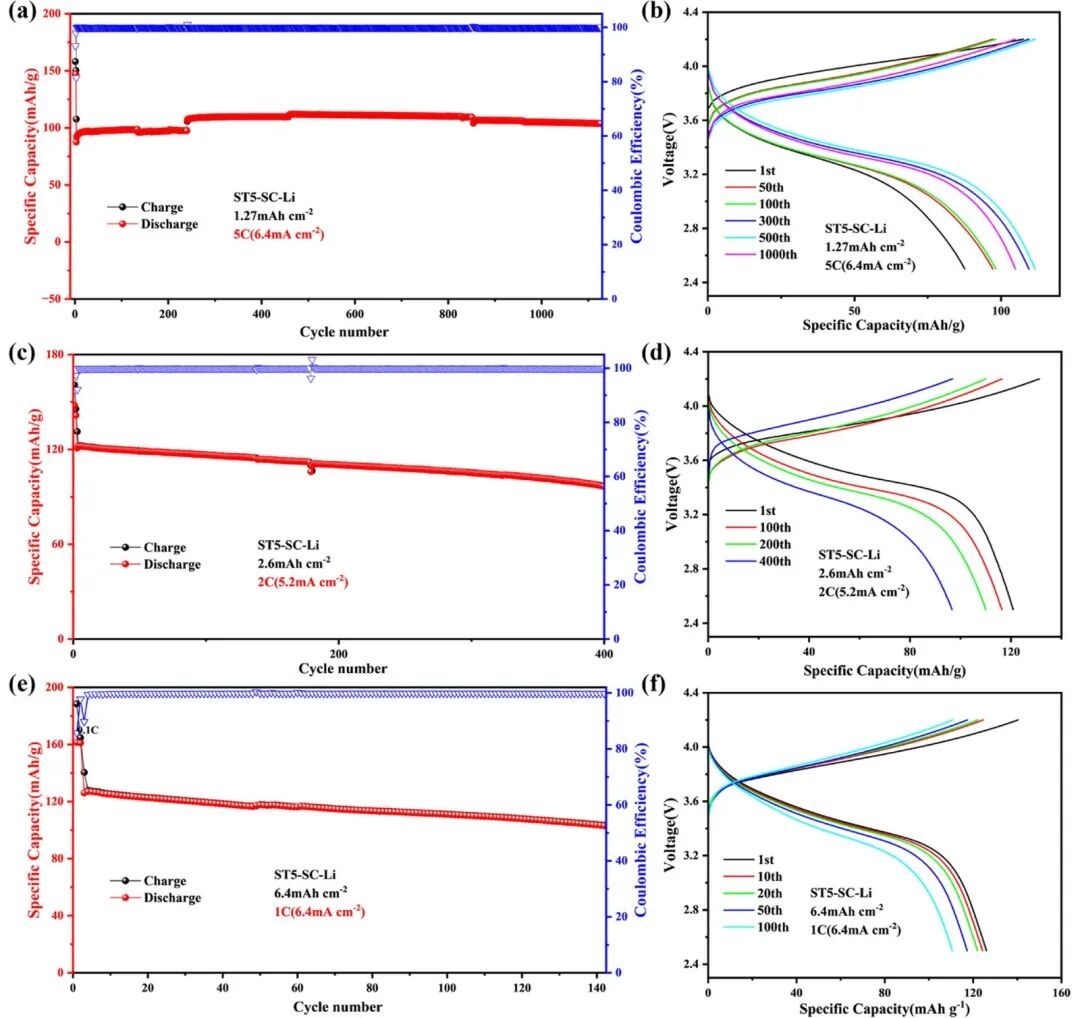
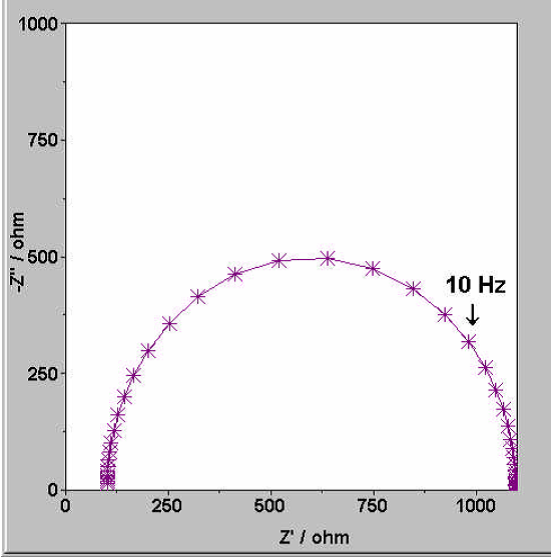
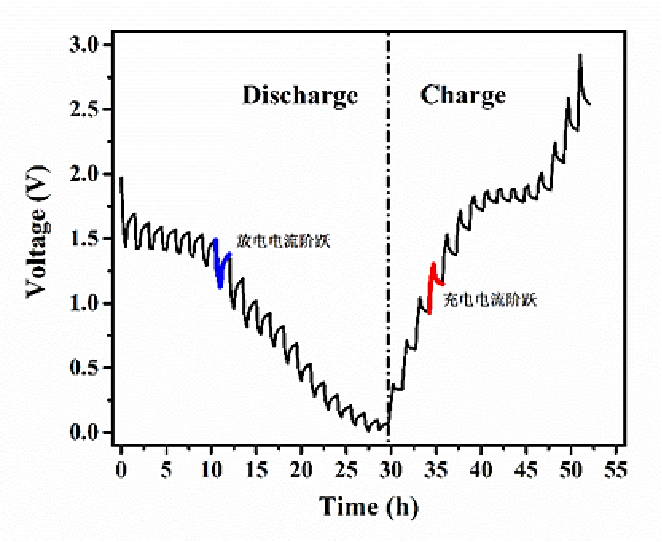
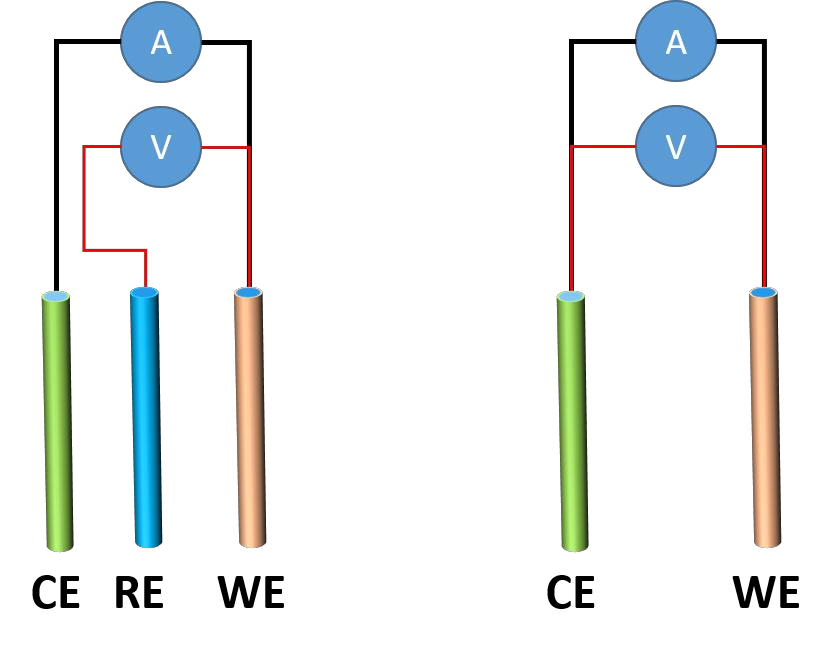
Alligator Clips in Battery Testing: From Selection to Use Considerations 2024
When it comes to electrical testing and measurement, precision and reliability are paramount. One of the most overlooked yet crucial components in this domain are alligator clips, also known as crocodile clips. These versatile tools are indispensable for creating temporary electrical connections, and they play a significant role in the testing of batteries, particularly the widely used 18650 lithium batteries. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of alligator clips, their various applications in battery testing, and how they impact the testing outcomes, using the 18650 lithium battery as a case study. Characteristics of alligator clips Shape and functionality Alligator clips derive their name from