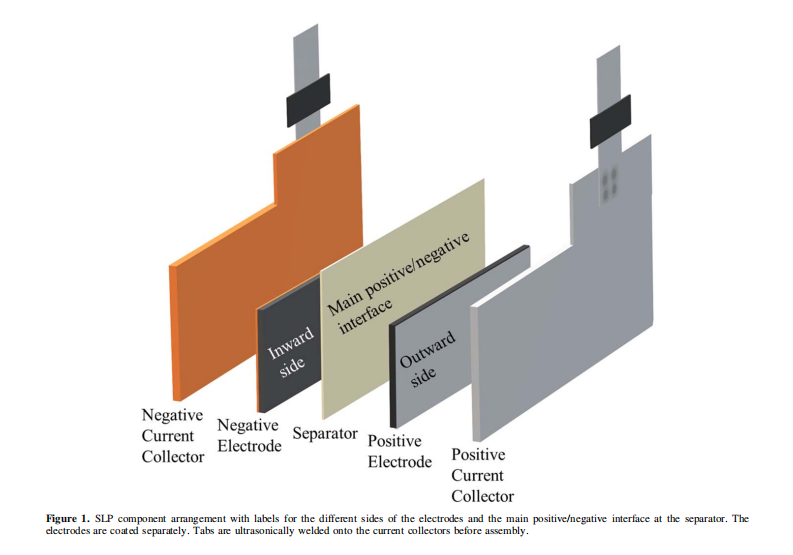
A Guide to Making Highly Reproducible Li-Ion Single-Layer Pouch Cells for Academic Researchers Published August 23, 2023.
A Guide to Making Highly Reproducible Li-Ion Single-Layer Pouch Cells for Academic Researchers Publication Details Title: A Guide to Making Highly Reproducible Li-Ion Single-Layer Pouch Cells for Academic Researchers Journal: Journal of The Electrochemical Society (Impact Factor: 3.9) DOI: 10.1149/1945-7111/aceffc Research Team: Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Canada; NOVONIX Battery Technology Solutions. Research Summary: To address the performance gap between the coin cells commonly used in academia and industrial-grade multilayer pouch cells, this study proposes a fabrication method for single-layer pouch cells (SLPs) featuring a no-overhang design. By optimizing electrode alignment and packaging processes, this approach significantly enhances the reliability and industrial relevance of battery testing.