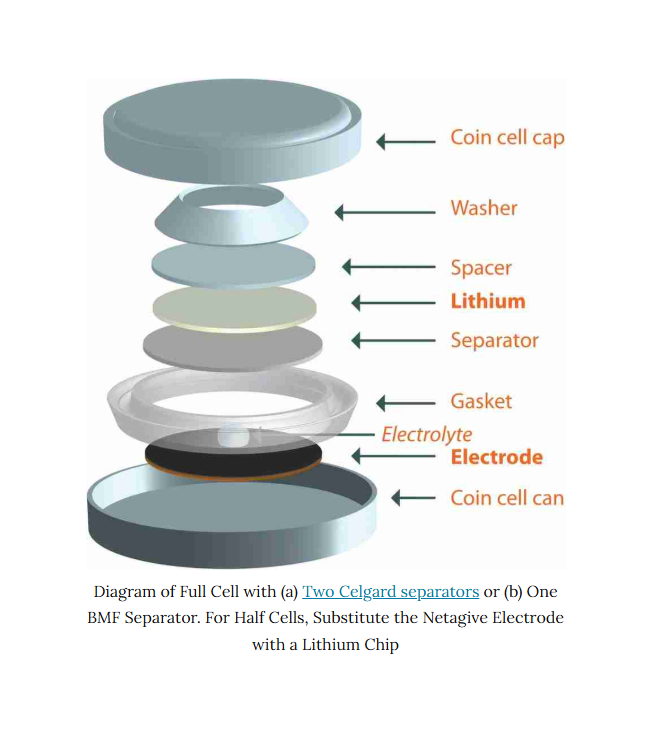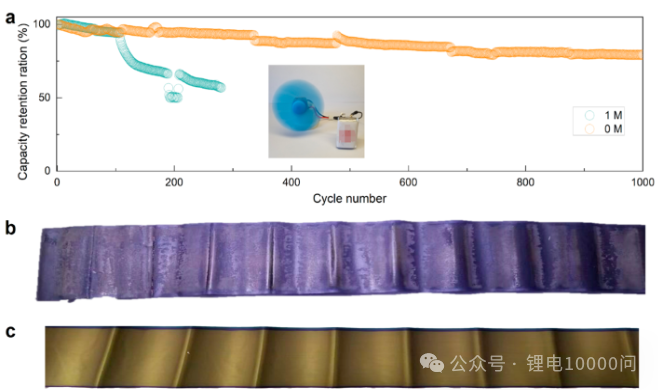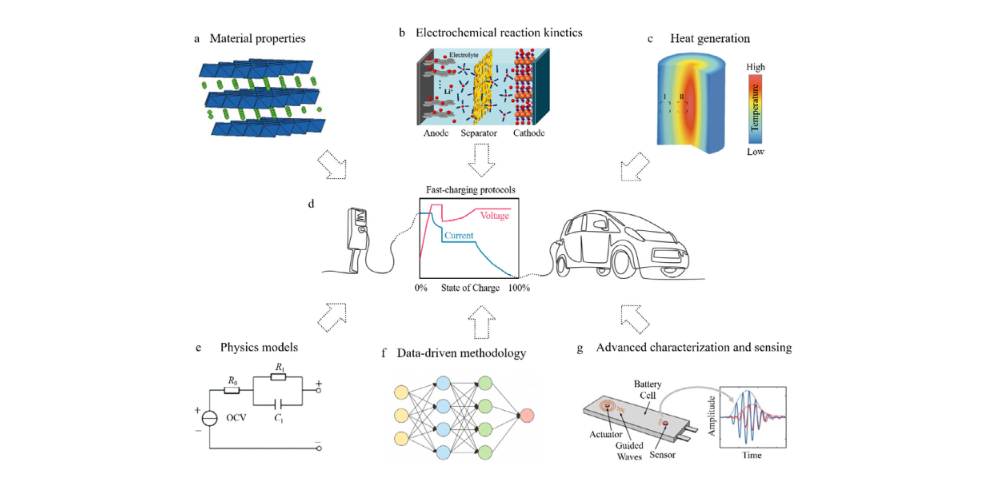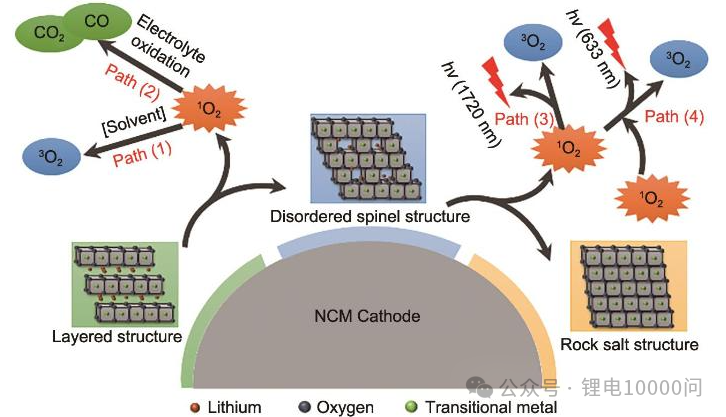
“Silent Alarms” in NCM Batteries: How 6 Key Gases Dictate Battery Safety and Longevity
“Silent Alarms” in NCM Batteries: The Interplay Between Gas Generation, Battery Safety, and Battery life During the battery formation stage—the final step before a brand-new NCM (Ternary) battery leaves the factory—the volume of gas discharged is enough to make any engineer frown with concern. These invisible gases are quietly dictating the battery’s future lifespan and its safety boundaries. As the market share of New Energy Vehicles (NEVs) surges, batteries now account for over 50% of a vehicle’s total cost, making safety and longevity the top priorities for consumers. Ternary lithium batteries, particularly high-nickel systems, are widely favored for their high energy density. However, the gas evolution that occurs during cycling